You can find out if your personal computer is compatible with Windows 11. You could use Microsoft’s PC Health Check App to do so. Or, you could look into the Windows Update section. If you are on the Windows 10 build 21H2, it would tell you if your system is compatible with Windows 11 or not.
And, the latest updated method to find PC’s compatibility with Windows 11 operating system is through the use of WhyNotWin11 app. This is an open source app that takes less than a minute to tell you about compatibility between your computer and Windows 11. You can read more about the WhyNotWin11 on this page, and you will find in-depth details about how you could install the app on your computer. The content will also help you decipher some of the more significant compatibility items on your computer.
However, a far better way is to try to find out the cause of incompatibility with Windows 11. This could help in isolating the cause and trying to implement a fix that would allow you to install Windows 11 on an incompatible personal computer. Before you upgrade Windows 10 to Windows 11, ensure that you have the backup of your user data and operating system files.

What are the eligibility requirements to run Windows 11?
We will split the requirements for Windows 11 in 2 sections:
Processor and System information
First, we need to find out if the processor on the system is compatible with Windows 11. Microsoft states that you must use a processor that runs at a clock speed 1 GHz or more. It has internal memory or RAM of at least 4 Gb and available disk storage of 64 Gb.
Most of these requirements can be checked by visiting the System—->about section on your computer.
- Click on Windows icon or Start
- In the search box, write ‘System’. Alternatively, open the control panel and select ‘System’
Choose System and you will see an about section that has Device Specifications, like the image below:
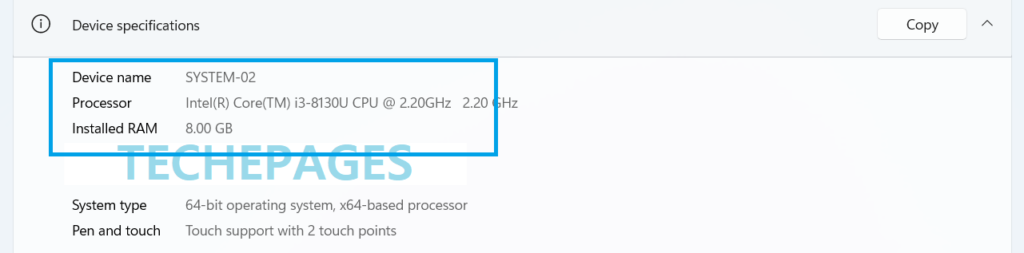
If you see a processor that is over 1 GHz in clock speed, and internal memory over 4 GB, then find out the available disk space on the computer. In most cases, available disk space should never be a problem. We only need 64 GB available space.
Do remember that most 7th generation Intel processors are incompatible with Windows 11. I will suggest checking out the Microsoft’s list of compatible PCs to ensure that your processor is compatible. Processor name is mentioned in the ‘Device Specifications’ under System icon of Control panel. In the image above, you will see the processor name is Intel I3-8130. This is an 8th generation processor of Intel.
To check your processor’s compatibility with Windows 11, check out this link for Intel processors that are compatible with Windows 11.
Once we know that the processor, RAM and hard drive space are compatible for Windows 11 installation or upgrade, we will move to the second section of eligibility.
Device Security
We will check for TPM, Secure boot and standard hardware security including UEFI and DEP.
To check your system’s compatibility with Windows 11,
- Click on Start and bring up the search box
- Type ‘Device Security’. This should bring up the Device Security app under the Control Panel—->System. You could also open the ‘Device Security’ option through the System icon on the control panel. Once you open, you will see a ‘Device Security’ screen shown below:
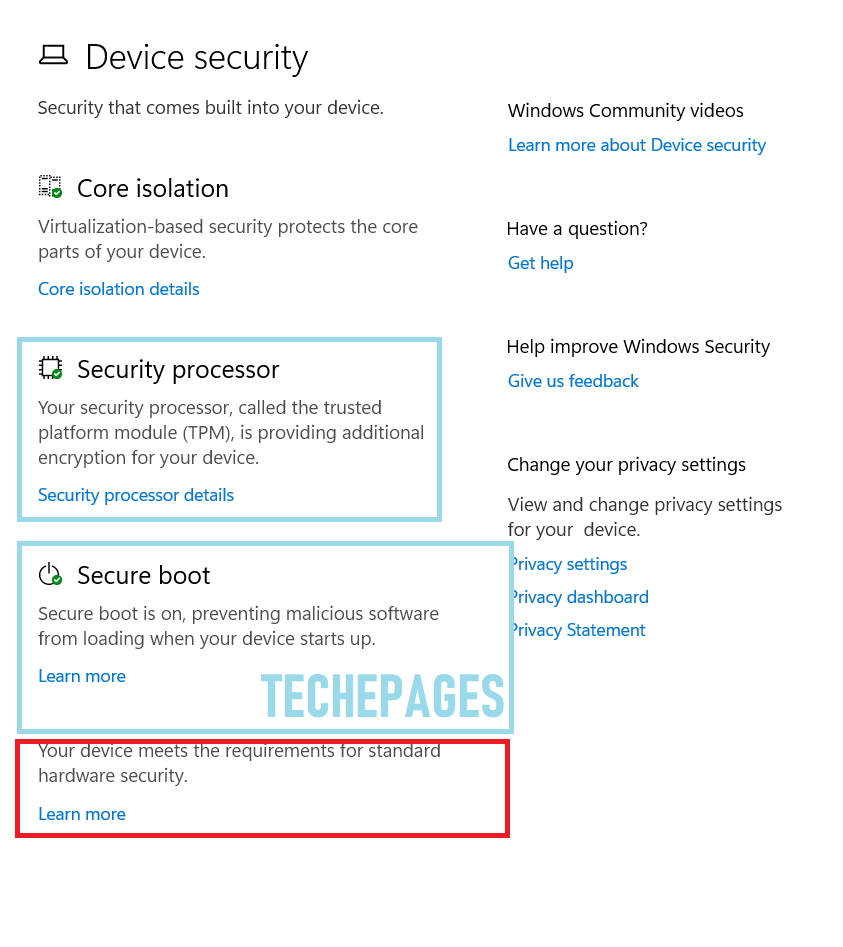
- Trusted Platform Module 2.0 – notice that the image above shows that the system has TPM.
- Secure Boot – notice that the image above shows that the system has ‘Secure Boot’
- DEP
- UEFI
While Microsoft clearly lays out the TPM and Secure boot status on the ‘Device Security’ screen, the DEP and UEFI are not individually reported. Rather, you have a status statement that shows
Your device meets the requirements for standard hardware security.
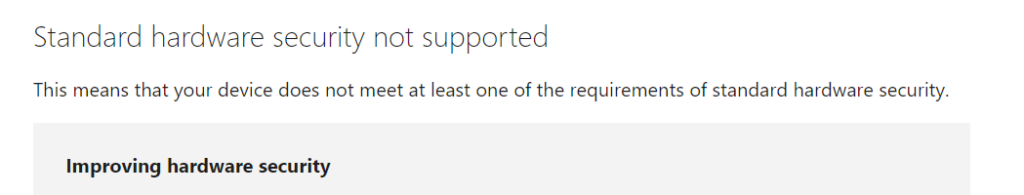
See the image above that shows that the device meets the requirements for standard hardware security. On a system that is incompatible, you will get a message that is displayed in the image below:
Summary
Finding out the system’s compatibility with Windows 11 is easily done with the System—> About and System—–> Device Security sections on the control panel. One could check the compatibility of processor, TPM, Secure boot and standard hard security eligibility from the Device Security screen of System.
Rajesh Dhawan is a technology professional who loves to blog about smart wearables, Cloud computing and Microsoft technologies. He loves to break complex problems into manageable chunks of meaningful information.